Honda’s CVT transmissions, understandably though unfairly, get lumped in with the unreliable reputation of CVTs in general, particularly from brands such as Nissan. However, the reliability of Honda CVT transmissions is often far more dependable, offering smoother performance and greater longevity, provided that it’s been maintained properly.
That said, while Honda’s CVTs are more reliable than most of its rivals, they still have their fair share of issues, including premature fluid degradation, CVT belt slippage, and the occasional software-related jerking. Nevertheless, with proper maintenance, including fluid changes, Honda CVTs could easily last over 150,000 miles without major issues.
Honda CVT Reliability
At a glance, Honda CVT transmissions offer you superb reliability, particularly if you practice regular maintenance and perform fluid changes. It may sound simple, but doing this alone could easily prevent some of the common issues (which we’ll discuss in more detail further below), such as:
| Common Issues | Symptoms | Estimated Repair Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Early Fluid Breakdown | Rough shifting, slipping gears | $80–$150 (fluid change) |
| Belt & Pulley Wear | Whining noise, loss of power | $1,500–$4,000 (repair) |
| Software & Sensor Issues | Jerking, delayed response | $100–$300 (reprogramming) |
| Transmission Overheating | Warning lights, limp mode activation | $500–$3,000 (cooling fix) |
Most of Honda’s current line-up, including their wide range of hybrid cars, come with a CVT transmission. While other options are available, such as an old-school H-pattern manual gearbox or a conventional automatic, these are the exception rather than the rule. Thankfully, since you can’t avoid them, Honda’s CVTs are actually pretty reliable, all things considered.
Honda CVT Problems And Fixes
So, the good news here is that Honda makes some of the most reliable CVTs on the market today. Few owners have made complaints about Honda CVT reliability issues, but it’s by no means as bad as some other brands, such as Nissan and their CVTs. However, it would be a good idea to understand more about how you can spot a CVT problem, should it appear.
This will help to better prepare you in case you need to send your car off for repairs. There are thankfully some very clear symptoms that can be exhibited should your Honda’s CVT start to fail. We don’t recommend driving your car around for much longer if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. With that in mind, here are some common symptoms of a failing CVT:
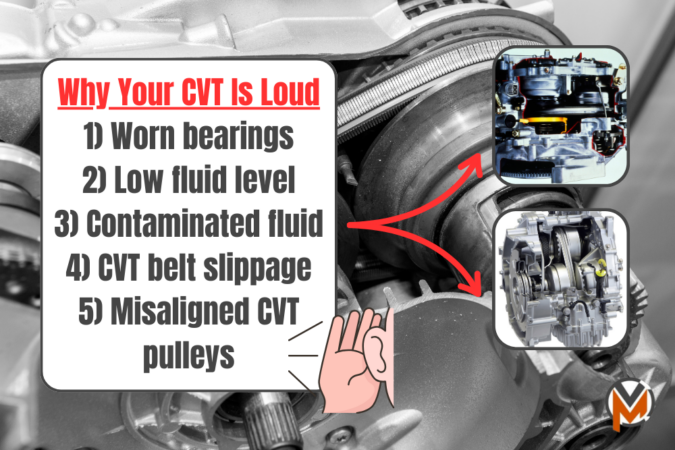
1. Transmission Running Louder Than Normal
As we’ve learned earlier, CVTs are a bit louder than the more conventional automatics owing to their design. However, these noises should be faint, and can simply be drowned out by your radio. If you notice it becoming progressively louder (loud rattling or whining noise while your car is running), this is a sign that your CVT starting to show signs of failure.
Aside from the loud rattling or whining noises (particularly when accelerating), you might also notice other sounds… 1) increased humming or rumbling noise while idling, or 2) sudden and odd changes to your car’s sound pattern during acceleration.
There are several reasons why your Honda’s CVT might become loud:
- Worn-out bearings
- Low transmission fluid levels
- Old or contaminated transmission fluid
- CVT belt slippage
- Misaligned CVT transmission pulleys
As to how much fixing these might cost you:
- Transmission fluid change ($100 to $250)
- CVT belt replacement ($200 to $500)
- Bearing replacement ($300 to $600)
- Complete CVT transmission replacement ($2,000 to $4,000)
- Mechanic diagnostic fees ($50 to $100)
2. Vibrations Or Shuddering Under Acceleration
One thing to note here is that some carmakers intentionally program a “step” feature into their CVTs. This simulates the feedback and sounds of more traditional gear changes. However, this feeling is different from the constant vibrations or transmission shudder that might point toward CVT failure. This is often caused by overheating of the CVT gearbox.
Excess heat can cause transmission mounts and bearings to wear out prematurely, causing all the shaking. Besides the consistent shudder or excessive vibrations (mainly under acceleration), you might also notice sudden jolts. Otherwise, you could also experience reduced power during acceleration or unusual clunking or thudding noises.
The underlying reasons why you notice these vibrations or shudders include:
- Overheating or continuous strain
- Worn-out transmission mounts
- Damaged or worn bearings
- Transmission fluid contamination
- Damaged or slipped CVT belt
To fix these, you might have to consider these expenses:
- Transmission fluid change ($100 to $250)
- Transmission mount replacement ($150 to $350)
- CVT bearing replacement ($300 to $600)
- CVT belt replacement ($2oo to $500)
- Mechanic diagnostic fees ($50 to $100)
3. Sluggish Acceleration Or Stalling While Driving
If your car is struggling to get up to speed, it is another sign that your Honda CVT transmission is on its way out. This slow acceleration happens when your car hesitates to change up a gear. Or, if you notice how your car won’t move in any gear at all. Ordinarily, CVTs should offer you a gradual and progressive build-up of power.
For some cars, significant component failure could also trigger the car to go into its “limp home” mode that restricts speed. Sometimes, CVT failure can cause the car to stall or shut down completely while driving. Other noteworthy symptoms include a lack of power, your car refusing to move at all in any gear, as well as unexpected stalling.
This acceleration or stalling issue might arise due to these CVT-borne faults:
- CVT belts damaged or worn out
- Contaminated or old transmission fluid
- Failed valve body or solenoid
- Faulty CVT transmission sensors
- Internal damage (gears or other components)
For a general idea of how much it might cost you to fix these underlying problems:
- Transmission fluid change ($100 to $250)
- CVT sensor replacement ($50 to $200)
- Valve body or solenoid repair ($200 to $600)
- Complete CVT transmission replacement ($2,000 to $4,000)
- Mechanic diagnostic fees ($50 to $100)
4. Burning Smell Coming From The Transmission
Although CVT transmissions have few running parts, they can still run hot. Without proper cooling or maintenance, they can still overheat. You can notice a particular burning smell from your car; a sign that something is running a lot hotter than it should be. Or, you might be able to check your car’s temperature gauge and see if there are any anomalies there.
Apart from an overheating transmission, that burning smell could also point to a transmission fluid leak on the hot exhaust. You mostly notice this after driving, and in some cases, you might even notice smoke or steam. More telling is experiencing transmission gear slippage while shifting up or down, as well as puddles, pointing to a transmission fluid leak.
There could be numerous underlying reasons why your transmission is overheating:
- Inefficient or compromised CVT cooling system
- Transmission fluid leakage
- Worn or contaminated transmission fluid
- Faulty CVT transmission cooling lines
- Bad CVT bearings or belts
To help you budget for a trip to the local workshop and fix your transmission, consider:
- Transmission fluid change ($100 to $250)
- CVT cooling system flush ($100 to $150)
- Transmission leak repair ($150 to $500)
- Cooling line replacement ($100 to $400)
- Mechanic diagnosis fees ($50 to $100)
5. Honda CVT Transmission Fluid Leaks
Just like a conventional gearbox, CVTs have their own transmission fluid to aid in lubrication and cooling. Overheating can cause parts of the cooling system to wear out prematurely. This includes cooling lines or seals. The result is a pinkish puddle underneath your car. Transmission fluid leaks are another sign of potential failure with your CVT gearbox.
As such, it can no longer provide the optimal amount of lubrication, as well as cooling for the CVT transmission. Some other related symptoms you might notice include seeing a pinkish puddle under your car, gear slippage while shifting, whining or humming noises, as well as dashboard warning lights, and a hot smell from the gearbox.
CVT transmission fluid leaks can originate from a wide range of underlying faults and issues:
- Old and worn transmission fluid seals
- Compromised CVT cooling lines
- Overfilled transmission
- Fault transmission pan or gasket
- Poorly installed transmission fluid filters
Solving these might involve the following expenses:
- Transmission fluid top-up ($50 to $100)
- Seal or gasket replacement ($200 to $600)
- CVT cooling line repair ($100 to $400)
- Transmission pan replacement ($100 to $300)
- Mechanic diagnostic fees ($50 to $100)
Other Honda CVT Transmission Issues
Besides the top 5 common Honda CVT reliability issues that we mentioned earlier, here are some other common transmission-related faults you might encounter with your Honda:
- Delay In Response – When you shift your Honda from “park” to “drive,” there should be an instant response. With a failing CVT, you might experience a noticeable delay. This hesitation poses a safety hazard, and it also signals a larger issue. A delayed response might be a symptom of a declining transmission control module or an issue with the transmission’s valve body.
- Warning Lights – If there’s an issue with your CVT, the transmission warning light or check engine light may illuminate. While these lights can be triggered for various reasons; a persistent warning light should never be ignored. Having the error codes read by a professional or an OBD scanner can quickly pinpoint if the issue is with the CVT.
- Poor Fuel Economy – One of the perks of CVT transmissions is better fuel efficiency. So, if you start to notice a decrease in miles per gallon, your CVT could be the culprit. When the CVT isn’t functioning optimally, the engine works harder, consuming more fuel. Keeping a close eye on your fuel consumption can indirectly hint at CVT problems.
- Inconsistent Movement – A smooth driving experience is a hallmark of CVTs. If you observe your Honda suddenly jerking or surging, especially under steady speeds, there’s cause for concern. This unpredictable behavior can be a symptom of transmission slipping due to low fluid levels, worn belts, or issues with sensors controlling the CVT.
- Difficulty Shifting Gears – While CVTs don’t have “gears” in the traditional sense, you might still feel a sensation similar to shifting. If this becomes noticeably difficult, or if the transitions become jarring, the CVT might be malfunctioning. Moreover, if your car struggles to find the right “gear” ratio or you feel constant up-and-down shifts, it’s a sign that something’s amiss.
Honda CVT Transmission Maintenance
So, even though Honda’s CVT transmissions feature fantastic reliability, relatively speaking to other CVTs, their lifespan heavily depends on you performing proper maintenance. Our research shows that some Honda CVT transmissions could easily last way over 150,000 to 200,000 miles before needing a rebuild or replacement.
Yet, we’ve also found plenty of other Honda CVT transmissions that experience issues way earlier, either due to neglect, poor maintenance, or harsh driving conditions. So, if you want to ensure that your Honda’s CVT lasts you a long time and offers a problem-free driving experience, here are some preventative maintenance tips that you should follow.
Preventative Maintenance Tips For Honda CVT Transmissions
Following proper maintenance could significantly improve the reliability of your Honda CVT transmission:
- Regular Fluid Changes – Honda CVT transmission fluid degrades over time, like any regular transmission, leading to slipping and overheating. So, make sure that you change the fluid every 30,000 to 50,000 miles using Honda HCF-2 CVT fluid for optimal performance.
- Avoid Aggressive Acceleration – Rapid throttle inputs can easily cause excessive belt and pulley strain. With that in mind, you ought to take your time to practice smooth and gradual acceleration to help reduce wear and tear.
- Monitor Transmission Cooling System – Overheating is a major cause of CVT failure. That said, you have to make sure that the radiator, transmission cooler, and transmission fluid levels are in good condition. This is especially so in warmer climates or with frequent stop-and-go driving.
- Update Transmission Software – Some Honda models regularly receive TCM (Transmission Control Module) updates that refine the CVT’s operation and prevent premature failures. Every once in a while, it’s not a bad idea for you to check for Honda service bulletins related to your vehicle’s model and model year.
- Listen for Early Warning Signs – Unusual whining noises, delayed response, and erratic RPM behavior can signal early CVT issues. So, pay close attention to these symptoms, because addressing minor problems early on could prevent complete transmission failure.
How Long Does A Honda CVT Last?
Of course, the reliability of a Honda CVT transmission does vary depending on the specific model, model year, and maintenance history. However, most Honda CVTs could easily last at least 120,000 to 200,000 miles before requiring major repairs. Here are some insights that we’ve learned from past and present owners:
- Well-maintained CVTs in some of Honda’s more popular Civics and Accords frequently surpass 150,000+ miles with minimal issues.
- Heavy city driving and towing reduce longevity, which sometimes leads to failures at around 80,000 to 120,000 miles if transmission fluid changes are ignored.
- A transmission cooler can help extend the CVT’s lifespan in high-heat environments. You could consider adding this upgrade to your car.
We’ve even learned that many Honda owners who follow strict transmission fluid change intervals and drive conservatively report 200,000+ miles on the original CVT. If you follow some of our earlier preventative maintenance tips, you too could maximize your CVT’s lifespan to get closer to that 200k mark. Or, at the very least, you could avoid premature failures.
Honda CVT Transmission vs Nissan vs Toyota vs Subaru
As we briefly mentioned earlier, CVTs vary significantly in reliability depending on the automaker. We’ve learned that Honda’s CVTs have a better reputation than Nissan’s, but still fall short of Toyota’s durability. Subaru’s CVTs are somewhere in between, with mixed reports based on model and year.
To help you figure out which is best for reliability, here’s a quick table that breaks down and compares the failure rates, maintenance costs, and reliability scores, between Honda’s CVTs and that of other Japanese brands:
| Brand | Common Issues | Average Lifespan | Maintenance Costs | Overall Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honda | Juddering, overheating, and delayed response | 120,000–200,000 miles | $250–$450 per service | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) |
| Nissan | Premature belt wear, overheating, or total failure | 60,000–120,000 miles | $300–$500 per service | ⭐⭐ (Poor) |
| Toyota | Occasional software issues, but otherwise highly durable | 150,000–250,000 miles | $200–$400 per service | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) |
| Subaru | Torque converter issues, as well as fluid degradation | 100,000–180,000 miles | $250–$500 per service | ⭐⭐⭐ (Average) |
Overall, the Honda CVT transmission sits in the upper-middle range of reliability, better than Nissan and Subaru but slightly behind Toyota. With proper maintenance, they could easily outlast the notorious Nissan Jatco CVT transmissions.
- Honda vs Nissan: Honda’s CVTs way, way more reliable than Nissan’s, which have a reputation for premature failures, particularly in Sentra, Altima, and Rogue models.
- Honda vs Toyota: Toyota’s Direct Shift CVTs use a launch gear, reducing strain on the belt system and making them some of the most durable CVTs on the market.
- Honda vs Subaru: Subaru CVTs can last rather long if properly maintained, but they did have issues in certain model years, especially with the Outback and Forester.



Brilliantly explained information on a very misunderstood and hated transmission
Thanks for the comment, Mike Lord!
Cheers, glad to bring some much-needed guidance and exposure on Honda’s CVTs, so hopefully, this would be of some help 🙂
my transmission guy doesn’t recommend them, but also recommends a trans service at 20k miles on conventional autos as well. he is the best in town so I believe. Honda is a solid company but a warrantee is a warrantee. You’ll get no love if it breaks after that.
Thanks for the comment, John Dougherty!
True, regardless of who you’re buying from, even from a brand that’s as solid as far as reliability is concerned as Honda, it’s always good to be wary. While their CVTs are more robust than some other brands like Nissan, it’s still a good idea to keep a close eye out.
At 60 years old I bought a 2016 Honda Accord with CVT for my wife. I now have 143,000 miles on it. Zero issues. Best car I’ve ever owned and that’s saying a lot as I got my CDL in 1977 and driven many vehicles in many countries. The Honda CVT is a great transmission compared to the automatics I’ve owned in the past. It provides a consistent 37mpg plus on trips. This is the first CVT I’ve owned and I’ll gladly own another. It has solid acceleration by keeping the engine in the power band. It’s much much smoother in deceleration as well. It well matches the 2.4l 4cly. For maintenance, I drain and fill three times every 30k miles. Drain and fill, drive around, repeat two times. Costs about $150 for 12 quarts (3.9 quarts for each drain and fill). Total capacity for the transmission is 8qts (7.6 liters). Doing it that way will get all but around 15% of the old trans fluid out of there. This Honda runs so well I guess I keep it for a while even though it’s well past where I usually get something newer for her because of reliability concerns. So far, there are NO indications this car is reaching the end of it’s service life. Hope you all experience the same that I have. Cheers.
Keith
I have been driving 30+ yrs old Mercedes Benz cars all my life, and you talk about changing cars every few years for reliability concerns lol. I’ve seen daily driver Mercedes 35+ yrs on almost a million kilometers.
Thanks for the comment, KBetts!
And cheers to you too for sharing your story! Hopefully, others would share a similarly positive experience as yours. From my experience, Honda’s CVTs are among the better ones out there as far as reliability is concerned.
Probably fine for a Civic, but there’s a reason why CVTs aren’t used in high-horsepower situations. I wish more companies would develop DCTs. THAT is the normal evolution of the torque converter transmission.
Thanks for the comment, Johnny S.!
Aye, DCTs are pretty awesome, although compared to CVTs and conventional torque converters, there are certainly pros and cons with any transmission. But I agree, in high horsepower applications, few can beat a proper manual gearbox or a CVT.
They can last 10 or AT LEAST 5 YEARS, ahaha are you joking ? Ppl need reliable cars that would last over 20-30 years, we are not millionaires to buy new cars like cellphones.
My daughter bought a 2014 Honda Civic CVT with 79k miles on it. There is a cap that had popped on top of the transmission and there is rubber breather opening that was clogged. Once it gets clogged I guess the pressure increases and the cap pops out. I cleaned the rubber opening cap, turned it sideways so mud does not get int again. Then I put electrical tape around the cap so it fits tighter in the opening. There were signs of auto fluid on top (some had spliced out). And there were lots of nuts on top of the transmission (squirrel or chipmunk, not sure). I was worried that maybe a bit had fallen inside through the cap opening. I changed the fluid (drain and flush) and replaced the automatic fluid filter. The fluid was very dark – it was probably never changed. After about 4K miles I looked at the color of the fluid again and it seemed dark again, so I changed it again. Very smooth so far. Told her not to do burnouts;-). Good mileage too. She is a student and does not have a Lot of money. She chose this instead of a Prius (she had a Prius before) and right after that gas prices shot up. I think all in all so far so good.
I plan on looking at the liquid color again next summer.
Thanks for the input, let us know what the fluid looks like when you check it again.
Great explanation. I owned a 2017 Honda CRV that had a CVT. Never had a problem with it. The car was slightly boring to drive, but I don’t think it was because of the CVT.
Just wanted to clear up one misconception. The 2003 Accord and 2001 Civic didn’t have CVTs. They came with manual or normal automatic transmissions, a 5 speed automatic for the Accord and a 4 speed automatic for the Civic. I know because I owned a 2003 Accord.
By the way, that Accord was extremely reliable. I sold it when it had well over 200,000 miles on it and never paid for anything other normal service costs over all those years.
Thanks for the comment, AdamE!
Cheers for the clarification, I forgot to note down that they didn’t have CVTs back then just yet. And great to hear that your Accord’s been running well all these years – they’re a pretty dependable bunch!
Yes. Honda introduced the new CVT in 2015 and all 4 cylinder cars in 2016 (except the turbo 2L Accord which had a 10-speed auto). This is Honda’s 2nd CVT as the first very bad one was in 2000 Civic HX which barely made it to 60k. Honda learned a LOT from that experience hence their new CVT is the best out there.